165 N Village Ave, Suite 4
Rockville Centre NY 11570
P: (516) 660-3911
F: (786) 565-6619
pathways.pt.ot@gmail.com
Medicare Provider
Most Major Credit Cards Accepted
Hours: By appointment only
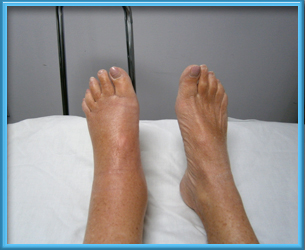
What is Lymphedema?
Swelling or edema is an accumulation of fluid in the soft tissues. Your body’s lymphatic system is part of your immune system, which protects you against infection and disease. It includes your spleen, thymus, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and lymph channels as well as your tonsils and adenoids.The principal function of the lymphatic system is to maintain the blood volume by returning fluid and proteins that flow from the blood capillaries to the tissues, back to the general circulation. With impairment of the lymphatic system these proteins and fluid are not adequately drained which can lead to the condition known as lymphedema.
Primary Lymphedema is a condition in which you are born with deficient lymphatic channels and/or nodes. It can present anytime from birth through adulthood but often manifests at puberty.
Secondary Lymphedema is most closely associated with the treatment of cancer. Lymph nodes are often removed to slow or prevent the spread of cancer. Treatment with radiation can be damaging to the lymphatics as well. Lymph cannot flow through the involved area causing edema to begin distal to the blockage. Edema can be present in arms, legs, trunk, or head and neck depending on the area of lymph flow disruption. Other causes of secondary lymphedema include trauma, infections, scars, burns, venous disease, and arterial or orthopedic surgery. Persistent edema after knee trauma or surgery is especially suspect as the inner thigh directly above the knee contains a high concentration of lymphatic vessels.
Each individual with chronic edema will experience different problems. Increased psychological distress, anxiety, depression, altered body image, reduced confidence, and difficulties with clothes are common. Individuals with lower limb swelling may have particular difficulties with footwear. Patients with foot and leg swelling are often forced to resort to unsuitable, loose fitting shoes or slippers that compound their reduced mobility.
As in any other condition the faster the problem is recognized and treated the better the outcome! Putting your head in the sand is not an option!
What to Look For (First Signs and Symptoms)
- Feelings of heaviness or tightness
- Aching or discomfort
- Restricted range of motion
- Recurring skin infections
- Swelling
- Hardening and thickening of the skin
Stages Of Lymphedema
Stage 0
There has been trauma to the lymphatics but they are still managing the lymphatic load. There are no signs of any lymphedema. However, patients in this stage are at risk of developing edema and should observe standard precautions.
Stage 1
Also known as the reversible stage because edema may recede overnight. Pitting, an indentation of the skin with direct pressure is common and mimics a vascular edema. Treatment initiated at this stage usually will reduce the extremity to normal size.
Stage 2
Also known as spontaneously irreversible lymphedema. Edema becomes non-pitting because of an increase in fibrous tissue. Volume increases and increased tissue density can be felt. Immune defense is decreased and infections of the skin (cellulitis) are common. Left untreated a cycle of increased edema and frequent cellulitis begins.
Stage 3
Also known as Elephantiasis. Limb volume continues to increase as well as fibrosis of tissue. The skin becomes thickened and dry often with cysts and fungus infections. Skin folds deepen. Return to normal size and texture is difficult to achieve and requires a prolonged series of treatment.
Precautions must be observed to minimize Lymphedema
- Scratches, cuts, burns and insect bites provide an entry point for an infection.
- Avoid contact with pets (claws).
- Avoid contact with prickly plants (wear gloves for gardening).
- Wear a thimble while sewing.
- Do not get cuticles cut when having a manicure/pedicure.
- Always wear an oven glove to remove items from the oven.
- Use only an electric razor
- Injections and blood pressure should not be done on affected side.
- Treat injuries vigorously by cleansing, applying antibiotic cream, and a clean dressing
- Seek medical care at first sign of infection.
- Heat worsens Edema
- Avoid exposure of the affected limb to the sun.
- Avoid hot baths/showers
- Do not use a jacuzzi or sauna
Other Precautions
- Avoid wearing tight clothing especially with elastic bands.
- Avoid wearing jewelry on the affected side.
- Avoid intense physical activity.